# Metrics Functionality
This document aims to guide users on how to use the metrics functionality of Sermant to monitor core metrics and custom metrics of plugins in real-time through monitoring tools such as Prometheus.
# Feature Introduction
To meet users' needs for real-time monitoring of Sermant's operational status and performance, as well as in-depth insights into plugin behavior, Sermant integrates Prometheus monitoring support. Users can monitor core metrics and custom metrics of plugins through monitoring tools like Grafana and set up metric-based alerts to proactively identify potential issues, ensuring service stability.
# Development Example
The following demonstrates how to create custom metrics for plugins based on the project from the Creating Your First Plugin document.
In the
io.sermant.template.TemplateInterceptorclass under thetemplate\template-pluginmodule, obtain the MetricService instance via ServiceManager to access the metrics service for custom metrics:MetricService metricService = ServiceManager.getService(MetricService.class);Use the APIs provided by MetricService to perform relevant operations, such as creating Counters, Gauges, Timers, and Summaries.
@Override public ExecuteContext doBefore(ExecuteContext context) { // Increment a custom plugin metric named 'custom.counter', adding two tags: 'type=http' and 'scope=myFirstPluginId' // The 'scope' tag is added through Tags.of().addScope(pluginId) metricService.counter("custom.counter", Tags.of("type", "http").addScope("myFirstPluginId")).increment(); // Increment a Sermant core metric named 'custom.counter2', adding two tags: 'service=heartbeat' and 'scope=core' // The 'scope' tag is added through Tags.of().addCoreScope() or Tags.of().addScope("core") // Note: Sermant core metrics cannot be created within plugins metricService.counter("custom.counter2", Tags.of("service", "heartbeat").addCoreScope()).increment(); return context; }Enable the Metric service by configuring the
agent/config/config.propertiesfile as follows:Note: The Metric service relies on the metrics endpoint exposed by the HTTP Server service, so the HTTP service must be enabled first.
# HTTP server switch agent.service.httpserver.enable=true # Metric service switch agent.service.metric.enable=trueConfigure Prometheus to scrape the metrics endpoint exposed by Sermant:
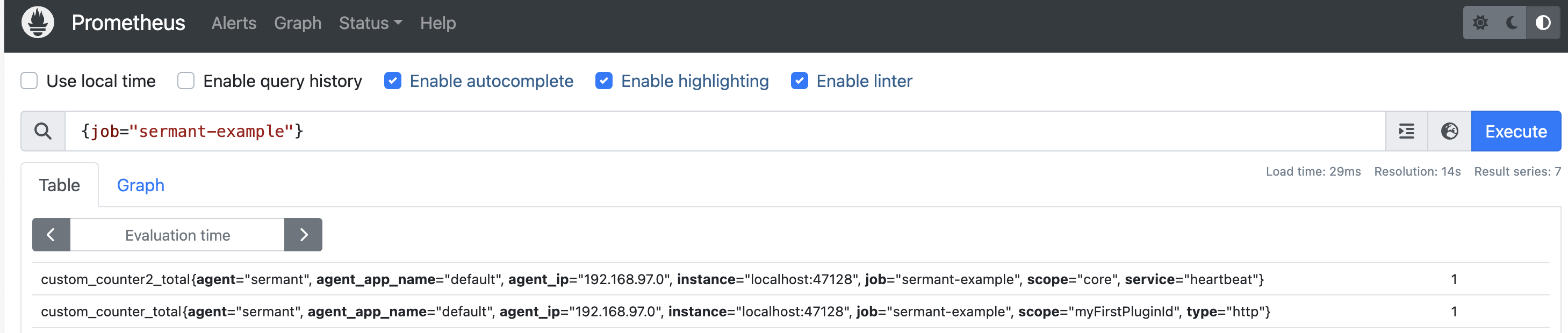
http://localhost:47128/sermant/metrics. In the Prometheusprometheus.ymlfile, configure as follows:scrape_configs: # job_name is the name of the scraping job, each job name should be unique - job_name: 'sermant-example' # metrics_path specifies the path to get metric data from sermant metrics_path: '/sermant/metrics' static_configs: # targets list includes all sermant agent addresses that need to be scraped, in the format 'host:port' - targets: ['localhost:47128']Start Prometheus and verify the collection of metric data, as shown in the following image:
# API & Configuration
# API
Obtain the Metric service:
MetricService metricService = ServiceManager.getService(MetricService.class);Custom Metrics
Developers can customize various types of metrics (Counter, Gauge, Timer, Summary) through the MetricService interface to monitor program runtime status.
Create a Counter type metric: used for counting, such as the number of requests. See Micrometer Counters (opens new window).
// Obtain a MetricService instance for subsequent metric operations MetricService metricService = ServiceManager.getService(MetricService.class); // Create and obtain a counter object named 'custom.counter' // For Sermant core metrics, use Tags.of().addCoreScope() or Tags.of().addScope("core") as the 'scope' tag // For plugin metrics, add 'pluginId' as the 'scope' tag through Tags.of().addScope(pluginId) // Adding the 'scope' tag here is to distinguish between sermant core metrics and sermant plugin metrics Counter counter = metricService.counter("custom.counter", Tags.of().addScope("myFirstPluginId")); // Increment the counter's value, typically used to record the number of occurrences, such as the number of requests or tasks completed counter.increment();Create a Gauge type metric: used to display current values, such as memory usage. See Micrometer Gauges (opens new window).
// Get MetricService instance for subsequent metric operations MetricService metricService = ServiceManager.getService(MetricService.class); // Create a gauge metric named "custom.gauge" // For Sermant core metrics, use Tags.of().addCoreScope() or Tags.of().addScope("core") as the scope tag // For plugin metrics, use Tags.of().addScope(pluginId) to add 'pluginId' as the scope tag Gauge gauge = metricService.gauge("custom.gauge", Tags.of().addScope("myFirstPluginId")); // Set the gauge value to 1, representing the current value of a specific measurement gauge.gaugeNumber(1);Create a Timer type metric: used to record time, such as method execution time. See Micrometer Timers (opens new window).
// Get MetricService instance for subsequent metric operations MetricService metricService = ServiceManager.getService(MetricService.class); // Create a timer named "custom.timer" to measure and record time // For Sermant core metrics, use Tags.of().addCoreScope() or Tags.of().addScope("core") as the scope tag // For plugin metrics, use Tags.of().addScope(pluginId) to add 'pluginId' as the scope tag // The scope tag is used to differentiate between core metrics and plugin metrics Timer timer = metricService.timer("custom.timer", Tags.of().addScope("myFirstPluginId")); // Record a specific duration, in this case, 10 seconds, using the timer timer.record(10L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);Create a Summary type metric: used to record data distribution, such as request latency. See Micrometer Distribution Summaries (opens new window).
// Get MetricService instance for subsequent metric operations MetricService metricService = ServiceManager.getService(MetricService.class); // Get a summary metric object named "custom.summary" to record subsequent data observations // For Sermant core metrics, use Tags.of().addCoreScope() or Tags.of().addScope("core") as the scope tag // For plugin metrics, use Tags.of().addScope(pluginId) to add 'pluginId' as the scope tag // The scope tag is used to differentiate between core metrics and plugin metrics Summary summary = metricService.summary("custom.summary", Tags.of().addScope("myFirstPluginId")); // Record a data observation value of 1.0 to the Summary metric object summary.record(1.0);
# Configuration
In the Sermant Agent package agent/config/config.properties, you can enable the Metric service using agent.service.httpserver.enable and agent.service.metric.enable. Other configurations for the Metric service are also included in this file:
# The metric type, currently supports prometheus.
metric.type=prometheus
# The maximum number of metrics.
metric.maxTimeSeries=1000
# Defines the common tag keys for metrics, with multiple keys separated by commas, the default values include "agent", "agent.app.name", "agent.ip" and "scope". For a complete list of available tag keys, refer to{@link io.sermant.core.service.metric.entity.MetricCommonTagEnum}.
metric.common.tag.keys=agent,agent.app.name,agent.ip,scope
The default common tags are agent, agent.app.name, agent.ip, and scope. Users can also specify the common tags to be used via metric.common.tag.keys.
Currently supported common tags are:
| Tag Key | Description |
|---|---|
| agent | Fixed value, always set to "sermant" |
| agent.app.name | The name of the Sermant application |
| agent.ip | The IP address of the machine running Sermant |
| scope | Specifies the scope of the Sermant metric. The default value is "undefined". For core metrics, use Tags.addCoreScope() to set the scope to "core". For plugin metrics, use Tags.addScope("pluginId") to set the scope to the plugin's ID |
| agent.service.name | The name of the Sermant service |
| agent.app.type | The type of the Sermant application |
| agent.artifact | The Sermant artifact |
| agent.version | The current version of Sermant |
# Notes
- The Metric service relies on the metrics endpoint exposed by the HTTP service, so ensure the HTTP service is enabled before using the Metric service.
- Ensure correct usage of the MetricService API in plugins to avoid inaccurate or missing metric data.
- When configuring Prometheus, ensure the correct HTTP server address and port for Sermant are set so that Prometheus can retrieve metric data from Sermant.
